General Formula of Alkane
The more general method omits only the terminal e of the substituent name but requires explicit numbering of each yl prefix even at position 1 except for -ylidyne which as a triple bond must terminate the substituent carbon chain. These notes covers the complete syllabus of General Organic Chemistry Class 11 including competitive exams like JEE mains and advanced NEET and others.

Question Video Applying The General Formula For Alkane Chemical Formulas Nagwa
We own and operate 500 peer-reviewed clinical medical life sciences engineering and management journals and hosts 3000 scholarly conferences per year in the fields of clinical medical pharmaceutical life sciences business engineering and technology.

. Textbook solution for General Organic and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition 4th Edition by Janice Smith Chapter 149 Problem 1418P. The simplest alkane is methane with the formula ofCH4. Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C 6 H 6The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each.
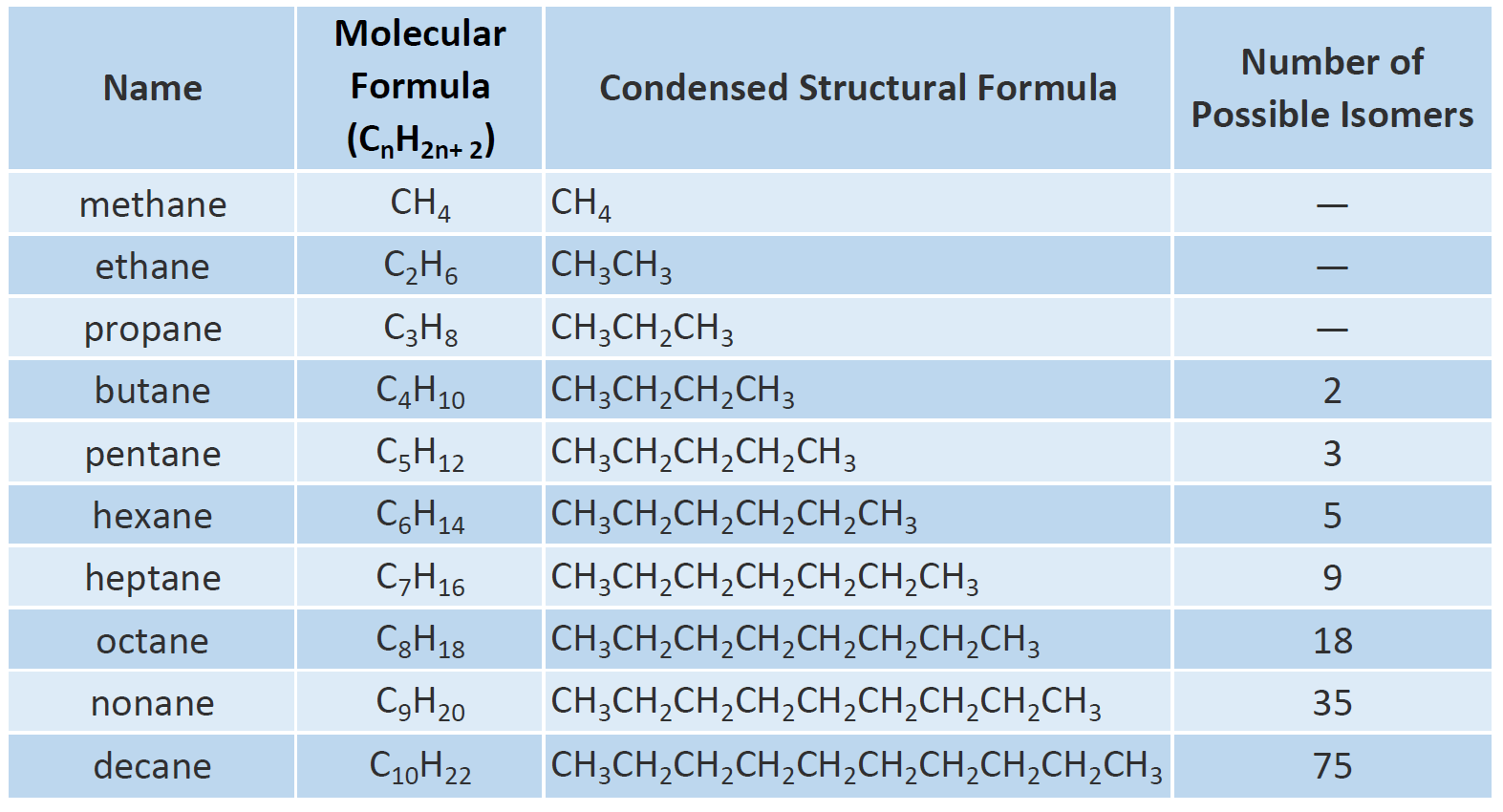
Alkanes are saturated organic compounds which are made up of C and H atoms. Alkanes Isomers compounds with same molecular formula Alkanes Isomers but different arrangement of atoms CH 4 methane C 2H 6 ethane C 3H 8 propane but different arrangement of atoms pp The molecular formula of an alkane with more than three carbons can give more than one structure C 4 butane butane and isobutane C 5 pentane pentane 2. The general formula for the alkanes is C n H 2n 2 where n is the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula C n H 2n-2Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes although the name acetylene also refers. Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil and is one of the elementary. Algebraic formula for a homologous series eg.
Nitrile Functional Group. Alcohols have the same general formula as alkanes but the structure of alcohol functional group is textOH called the hydroxyl group. GCSE Chemistry Single Science Organic chemistry learning resources for adults children parents and teachers.
Hydrocarbons are the principal constituents of petroleum and natural gas. They serve as fuels. When naming organic acids.
Pentan-1-yl is an example of a name by this method and is synonymous with pentyl from the previous guideline. Paraffins containing fewer than 5 carbon atoms per molecule are usually gaseous at room temperature those having 5 to 15 carbon atoms are. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.
Saturated hydrocarbons are the simplest of the hydrocarbon types. In organic chemistry an alkane or paraffin a historical trivial name that also has other meanings is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbonIn other words an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carboncarbon bonds are single. We are an Open Access publisher and international conference Organizer.
Hexane is an alkane. The paraffins are major constituents of natural gas and petroleum. If a simple unbranched alkane is converted to a cycloalkane two hydrogen atoms one from each end of the chain must be lost.
Alkanes have the general formula of CnH2n2. The most common alcohol known as ethanol is used in alcoholic drinks fuel gasoline a preservative for biological specimens and a solvent for paints and drugs. Alkane contains sp3 hybridized carbon atoms with four sigmas σ bonds every hydrogen atom is connected with one of the carbon atom.
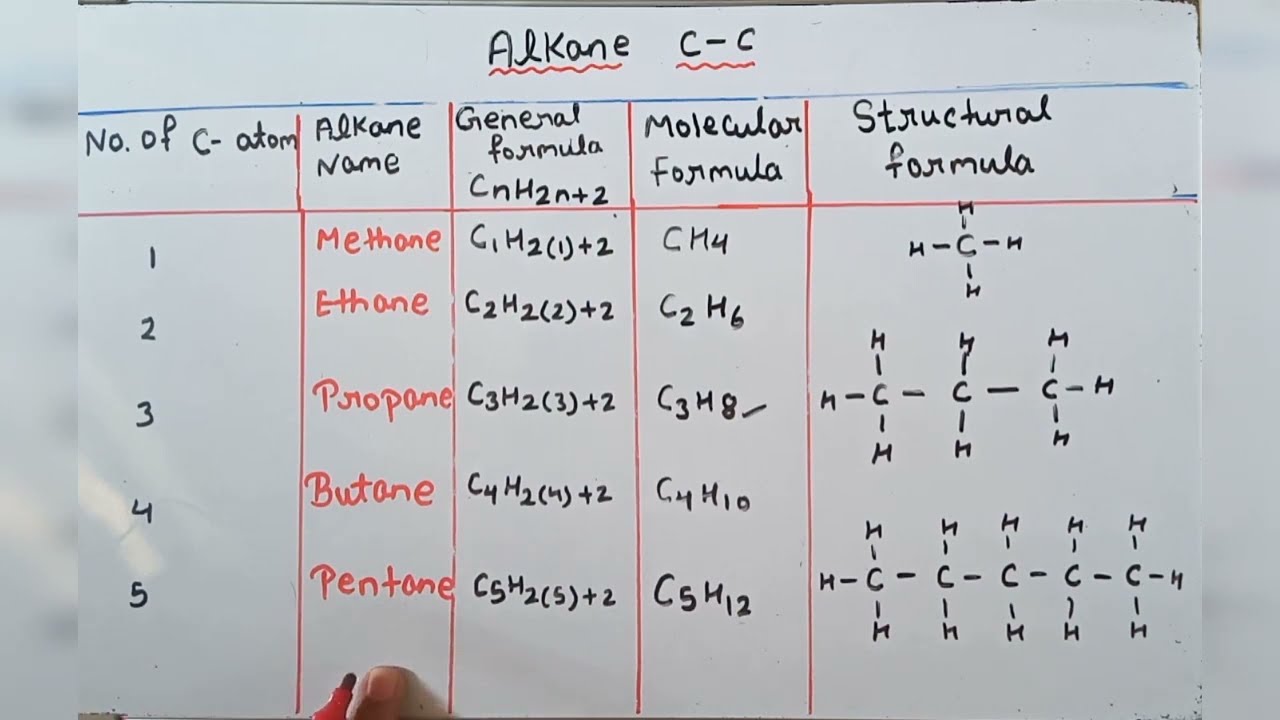
Read complete General Organic Chemistry notes for Class 11 Chemistry. General Rules for IUPAC Nomenclature. The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n 2.
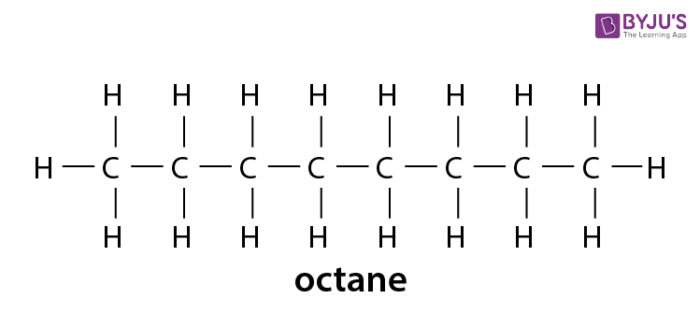
The structural formula of an eight-carbon alkane is C 8H 18 and the molecular formula is C 8 H 18. As defined by IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry the classifications for hydrocarbons are. Normal paraffins or normal alkanes are simply written as n-paraffins or n-alkanes and they are open straight-chain saturated hydrocarbons.
The carbon atoms join together to form the framework of the compound and the hydrogen atoms attach to them in many different configurations. Start your trial now. We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts.
You can also read. Natural gas and petroleum contain a large amount of paraffin. Word root denotes the number of carbon atoms present in the principal chain which is the longest possible chain of carbon atoms.
In chemistry and thermodynamics calorimetry from Latin calor heat and Greek μέτρον metron measure is the science or act of measuring changes in state variables of a body for the purpose of deriving the heat transfer associated with changes of its state due for example to chemical reactions physical changes or phase transitions under specified constraints. There are strong bonds or primary. Propanenitrile ethane-12-diol propanedioic acid propane-123-triol pentane-24-dione.
Some types of oils and waxes are the examples of alkanes with many carbon atoms number. Any of the saturated hydrocarbons with the general formula C n H 2n2 where C is a carbon atom H is a hydrogen atom and n is an integer is referred to as a paraffin hydrocarbon. These are very detailed and comprehensive notes developed by team of expert faculties.
The last yellow shaded column gives the general formula for a cycloalkane of any size. Hence the general formula for a. Paraffins are also called alkanes and have the general formula of C n H 2n2 where n is the number of carbon atoms in a given moleculeParaffins are divided into two groups of normal and isoparaffins.
There is no limit of how much carbons can be tied together. Hydrocarbon any of a class of organic chemical compounds composed only of the elements carbon C and hydrogen H. According to the IUPAC system the name of an organic compound in general consists of the following three parts.
Functional Groups This is the general structure of an aycl halide functional group where X is a halogen atom. General Structure or Formula. The formula for acyclic saturated hydrocarbons ie alkanes is C n H 2n2.
Or alkane containing an atom of a halogen such as chlorine bromine or fluorine. Shows the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in the compound. A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compoundsThe bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bondsThe strength of chemical bonds varies considerably.
Prefix i Word Root. The general formula for a nitrate is RONO 2. If a simple unbranched alkane is converted to a cycloalkane two hydrogen atoms one from each end of the chain must be lost.
First week only 499. It also can be more than 10 carbon atoms. They are composed entirely of single bonds and are saturated with hydrogen.
Used then do not remove the the e from the stem alkane name eg. Alkanes have the general chemical formula C n H 2n2The alkanes range in complexity from. Hence the general formula for a.
In organic chemistry an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carboncarbon triple bond. The last yellow shaded column gives the general formula for a cycloalkane of any size. Paraffin hydrocarbon also called alkane any of the saturated hydrocarbons having the general formula CnH2n2 C being a carbon atom H a hydrogen atom and n an integer.
623 The most general form of saturated. Its molecules contain six carbon atoms.
Alkanes Formula Definition Structure Properties List Of Alkanes Videos Examples And Faqs Of Alkanes
Ch105 Chapter 7 Alkanes And Halogenated Hydrocarbons Chemistry
Alkane Molecular Structural General Formula Youtube

Class 10 General Formula Of Alkane Alkene Alkyne Tx Academy Youtube
0 Response to "General Formula of Alkane"
Post a Comment